All Available Options
This section contains an exhaustive list of all Scancode options, arranged in various sections. The sections are as follows:
Basic Scan Options
Core Scan Options
Output Formats
Controlling Output and Filters
Pre-Scan Options
Post-Scan Options
There’s also another section for extractcode options.
The order of the sections and all their options is the same as in the Help text, available in the command line.
All “Basic” Scan Options
Option lists are two-column lists of command-line options and descriptions, documenting a program’s options. For example:
- -c, --copyright
Scan
<input>for copyrights.Sub-Options:
--consolidate
- -l, --license
Scan
<input>for licenses.Sub-Options:
--license-references--license-text--license-text-diagnostics--license-diagnostics--license-url-template TEXT--license-score INT--license-clarity-score--consolidate--unknown-licenses
- -p, --package
Scan
<input>for packages.Sub-Options:
--consolidate
- --system-package
Scan
<input>for installed system package databases.- --package-only
Scan
<input>for system and application only for package metadata, without license/ copyright detection and package assembly.- -e, --email
Scan
<input>for emails.Sub-Options:
--max-email INT
- -u, --url
Scan
<input>for urls.Sub-Options:
--max-url INT
- -i, --info
Scan for and include information such as:
Size,
Type,
Date,
Programming language,
sha1 and md5 hashes,
binary/text/archive/media/source/script flags
Additional options through more CLI options
Sub-Options:
--mark-source
Note
Unlike previous 2.x versions, -c, -l, and -p are not default. If any combination of these
options are used, ScanCode performs only that specific task, and not the others.
scancode -l scans only for licenses, and doesn’t scan for copyright/packages/general
information/emails/urls. The only notable exception: a --package scan also has
license information for package manifests and top-level packages, which are derived
regardless of --license option being used.
Note
These options, i.e. -c, -l, -p, -e, -u, and -i can be used together. As in, instead of
scancode -c -i -p, you can write scancode -cip and it will be the same.
- --generated
Classify automatically generated code files with a flag.
- --max-email INT
Report only up to INT emails found in a file. Use 0 for no limit. [Default: 50]
Sub-Option of:
--email- --max-url INT
Report only up to INT urls found in a file. Use 0 for no limit. [Default: 50]
Sub-Option of:
--url- --license-score INTEGER
Do not return license matches with scores lower than this score. A number between 0 and 100. [Default: 0] Here, a bigger number means a better match, i.e. Setting a higher license score translates to a higher threshold (with equal or smaller number of matches).
Sub-Option of:
--license- --license-text
Include the matched text for the detected licenses in the output report.
Sub-Option of:
--licenseSub-Options:
--license-text-diagnostics
- --license-url-template TEXT
Set the template URL used for the license reference URLs.
In a template URL, curly braces ({}) are replaced by the license key. [Default: default: https://scancode-licensedb.aboutcode.org/{}]
Sub-Option of:
--license- --license-text-diagnostics
In the matched license text, include diagnostic highlights surrounding with square brackets [] words that are not matched.
Sub-Option of:
--licenseand--license-text- --license-diagnostics
In license detections, include diagnostic details to figure out the license detection post processing steps applied.
Sub-Option of:
--license- --unknown-licenses
[EXPERIMENTAL] Detect unknown licenses.
Sub-Option of:
--license
All Extractcode Options
This is intended to be used as an input preparation step, before running the scan. Archives found in an extracted archive are extracted recursively by default. Extraction is done in-place in a directory named ‘-extract’ side-by-side with an archive.
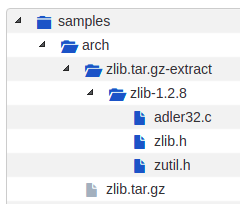
To extract the packages in the samples directory
extractcode samples
This extracts the zlib.tar.gz package:
- --shallow
Do not extract recursively nested archives (e.g. Not archives in archives).
- --verbose
Print verbose file-by-file progress messages.
- --quiet
Do not print any summary or progress message.
- -h, --help
Show the extractcode help message and exit.
- --about
Show information about ScanCode and licensing and exit.
- --version
Show the version and exit.
scancode-reindex-licenses Usage
Usage: scancode-reindex-licenses [OPTIONS]
Reindex scancode licenses and exit
Options
- --all-languages
[EXPERIMENTAL] Rebuild the license index including texts all languages (and not only English) and exit.
- --only-builtin
Rebuild the license index excluding any additional license directory or additional license plugins which were added previously, i.e. with only builtin scancode license and rules.
- --additional-directory DIR
Include this directory with additional custom licenses and license rules in the license detection index.
- --load-dump
Load all license and rules from their respective files and then dump them back to those same files.
- -h, --help
Shows the options and explanations.
All “Core” Scan Options
- -n, --processes INTEGER
Scan
<input>using n parallel processes. [Default: 1]- -v, --verbose
Print verbose file-by-file progress messages.
- -q, --quiet
Do not print summary or progress messages.
- --timeout FLOAT
Stop scanning a file if scanning takes longer than a timeout in seconds. [Default: 120]
- --from-json
Load codebase from one or more existing JSON scans.
- --max-in-memory INTEGER
Maximum number of files and directories scan details kept in memory during a scan. Additional files and directories scan details above this number are cached on-disk rather than in memory. Use 0 to use unlimited memory and disable on-disk caching. Use -1 to use only on-disk caching. [Default: 10000]
- --max-depth INTEGER
Descend at most INTEGER levels of directories including and below the starting point. INTEGER must be positive or zero for no limit. [Default: 0]
All Scan Output Options
- --json FILE
Write scan output as compact JSON to FILE.
- --json-pp FILE
Write scan output as pretty-printed JSON to FILE. This is one of the recommended output formats and contains all the data scancode can show along with the YAML output format.
- --json-lines FILE
Write scan output as JSON Lines to FILE.
- --yaml FILE
Write scan output as YAML to FILE. This is one of the recommended output formats and contains all the data scancode can show along with the JSON output format.
- --csv FILE
DEPRECATED: Write scan output as CSV to FILE. This option is deprecated and will be replaced by new CSV and tabular output formats in the next ScanCode release. Visit this issue for details, and to provide input and feedback: https://github.com/nexB/scancode-toolkit/issues/3043
- --html FILE
Write scan output as HTML to FILE.
- --custom-output
Write scan output to FILE formatted with the custom Jinja template file.
Mandatory Sub-option:
--custom-template FILE
- --custom-template FILE
Use this Jinja template FILE as a custom template.
Sub-Option of:
--custom-output- --debian FILE
Write scan output in machine-readable Debian copyright format to FILE.
- --spdx-rdf FILE
Write scan output as SPDX RDF to FILE.
- --spdx-tv FILE
Write scan output as SPDX Tag/Value to FILE.
- --html-app FILE
[DEPRECATED] Use
scancode-workbenchinstead. Write scan output as a mini HTML application to FILE.- --cyclonedx FILE
Write scan output as a CycloneDx 1.3 BOM in pretty-printed JSON format to FILE
- --cyclonedx-xml FILE
Write scan output as a CycloneDx 1.3 BOM in pretty-printed XML format to FILE
Warning
The html-app feature has been deprecated and you should use Scancode Workbench instead to visualize scan results. The official Repository link. Also refer How to Visualize Scan results.
All “Output Control” Scan Options
- --strip-root
Strip the root directory segment of all paths.
- --full-root
Report full, absolute paths.
Note
The options --strip-root and --full-root can’t be used together, i.e. Any one option
may be used in a single scan.
Note
The default is to always include the last directory segment of the scanned path such that all paths have a common root directory.
- --ignore-author <pattern>
Ignore a file (and all its findings) if an author contains a match to the
<pattern>regular expression.- --ignore-copyright-holder <pattern>
Ignore a file (and all its findings) if a copyright holder contains a match to the
<pattern>regular expression.
Note
Note that this both the options --ignore-author and --ignore-copyright-holder will
ignore a file even if it has other scanned data such as a license or errors.
- --only-findings
Only return files or directories with findings for the requested scans. Files and directories without findings are omitted (file information is not treated as findings).
All “Pre-Scan” Options
- --ignore <pattern>
Ignore files matching
<pattern>.- --include <pattern>
Include files matching
<pattern>.- --classify
Classify files with flags telling if the file is a legal, or readme or test file, etc.
Sub-Options:
--license-clarity-score--tallies-key-files
- --facet <facet_pattern>
Here
<facet_pattern>represents<facet>=<pattern>. Add the<facet>to files with a path matching<pattern>.Sub-Options:
--tallies-by-facet
All “Post-Scan” Options
- --mark-source
Set the “is_source” flag to true for directories that contain over 90% of source files as direct children and descendants. Count the number of source files in a directory as a new “source_file_counts” attribute
Sub-Option of:
--url- --consolidate
Group resources by Packages or license and copyright holder and return those groupings as a list of consolidated packages and a list of consolidated components. The –consolidate option will be deprecated in a future version of scancode-toolkit as top level packages now provide improved consolidated data.
Sub-Option of:
--copyright,--licenseand--packages.- --filter-clues
Filter redundant duplicated clues already contained in detected licenses, copyright texts and notices.
- --license-clarity-score
Compute a summary license clarity score at the codebase level.
Sub-Option of:
--classify.- --license-policy FILE
Load a License Policy file and apply it to the scan at the Resource level.
- --summary
Summarize scans by providing declared origin information and other detected info at the codebase attribute level.
- --tallies
Summarize license, copyright and other scans at the codebase level with occurrence counts.
Sub-Options:
--tallies-by-facet--tallies-key-files--tallies-with-details
- --tallies-by-facet
Summarize license, copyright and other scans and group the results by facet.
Sub-Option of:
--talliesand--facet.- --tallies-key-files
Summarize license, copyright and other scans for key, top-level files, with occurrence counts. Key files are top-level codebase files such as COPYING, README and package manifests as reported by the
--classifyoption: “is_legal”, “is_readme”, “is_manifest” and “is_top_level” flags.Sub-Option of:
--classifyand--summary.- --tallies-with-details
Summarize license, copyright and other scans at the codebase level with occurrence counts, while also keeping intermediate details at the file and directory level.